Posted in: 10/31/2023
The development of a personalized methodology for monitoring hot spots and analyzing territorial data in the Pantanal biome and in the Pantanal brigade areas is the latest positive result of the already well-known partnership between Synergia Socioambiental and the SOS Pantanal Institute in favor of the biome .
Named “Painel Aracuã ”, in honor of the native bird of the Pantanal that echoes a characteristic song in the territory, the initiative relies on the use of technology and accurate data analysis to monitor significant changes in the physical environment of the Pantanal and, thus, facilitate understanding how they behave during the months, helping to predict the following months and to draw up fire prevention and combat strategies .
Monitoring varied data , including data on the history of recorded hot spots, vegetation quality, terrain characteristics, existing infrastructure and preventive actions adopted can play a fundamental role in the region.
Through remote detection systems , such as NASA satellites and terrestrial sensors, it is possible to identify the locations where fires are occurring. This data allows for a quick and efficient response , directing available resources to affected areas and facilitating firefighting in the early stages , when the spread is more controllable, minimizing damage.
Furthermore, continuous monitoring helps to analyze occurrence patterns, identify areas of greatest risk and implement more effective preventive measures, establishing fundamental guidelines for managing combat teams , allocating resources and defining strategies. action against fire.
In this way, the Aracuã Panel , in addition to recording the history of events and presenting data in almost real time, helps the work and validates the importance of the Pantanal brigades – also favoring the identification of areas with more concentrated hot spots that are not yet being attended to by the brigades – enabling the protection of lives, ecosystems and properties in the monitored regions.

The Panel’s analyzes apply to the Paraguay Basin , where the Pantanal biome is contained and to the areas of the 24 Pantanal brigades linked to SOS Pantanal , and monitoring has been carried out since May this year.
It is important to highlight that the Aracuã Panel is one of the stages of the Aracuã System , which also has the “ Aracuã Alert” – a program developed by SOS Pantanal that detects hot spots directly from the NASA system and sends a personalized alert directly to the smartphone of people and brigade members who live in the areas covered by the Pantaneiras Brigades.
The Aracuã Panel data is currently divided into a General Information Panel and a Panel by Brigade . They demonstrate that it is necessary to adopt a holistic approach , which integrates different sources of information to adopt preventive measures and act to mitigate the risks associated with forest fires.
In this way, the analysis and visualization of 4 groups of data essential to all territorial planning linked to fire control, combat and management occurs :
Therefore, monitoring hot spots is just one aspect of fighting forest fires , which, to be truly effective, requires the integration of various information, including data on vegetation, terrain characteristics, existing infrastructure and preventive actions taken.
Furthermore, adequate training of fire brigades , the involvement of local communities and the implementation of prevention policies are essential elements for efficiently fighting fires.
Produced monthly , the general panels contain a text with a summary analysis of the results of the published panel, the number of hot spots observed in the brigades per accumulated month of the year, the graph of hot spots in the brigades per month, the ranking of the brigades with more hot spots in the year and the map of the location of brigades and hot spots.
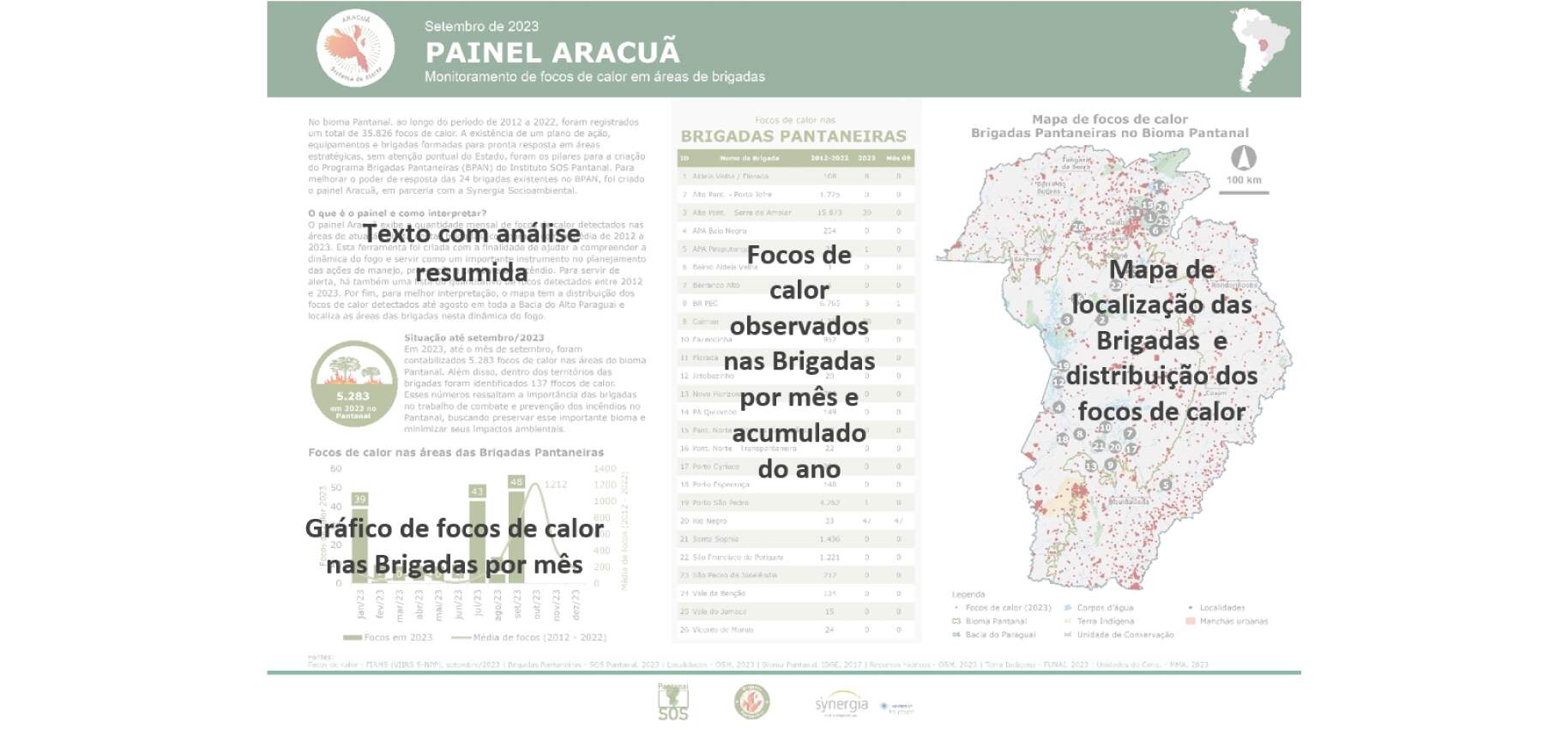
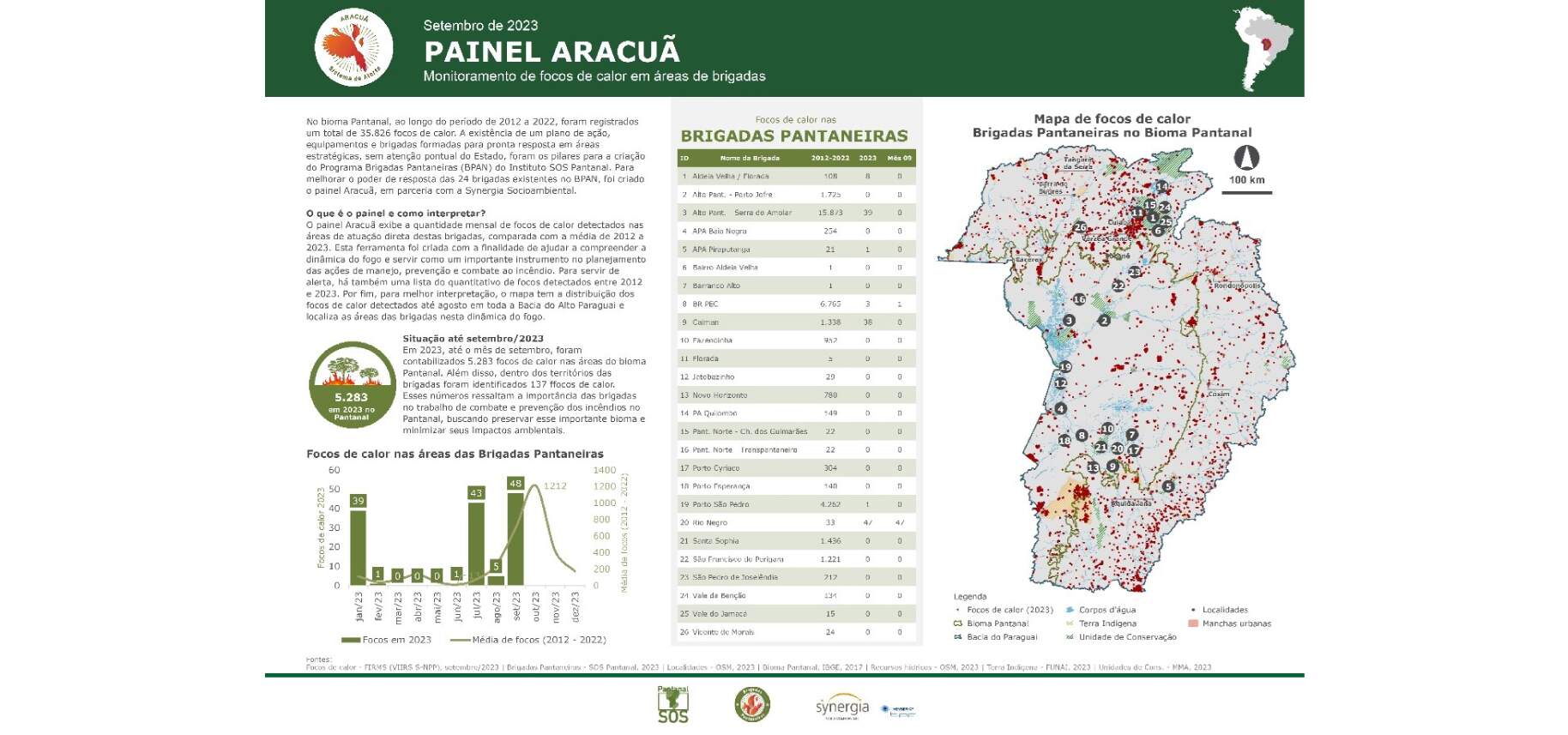
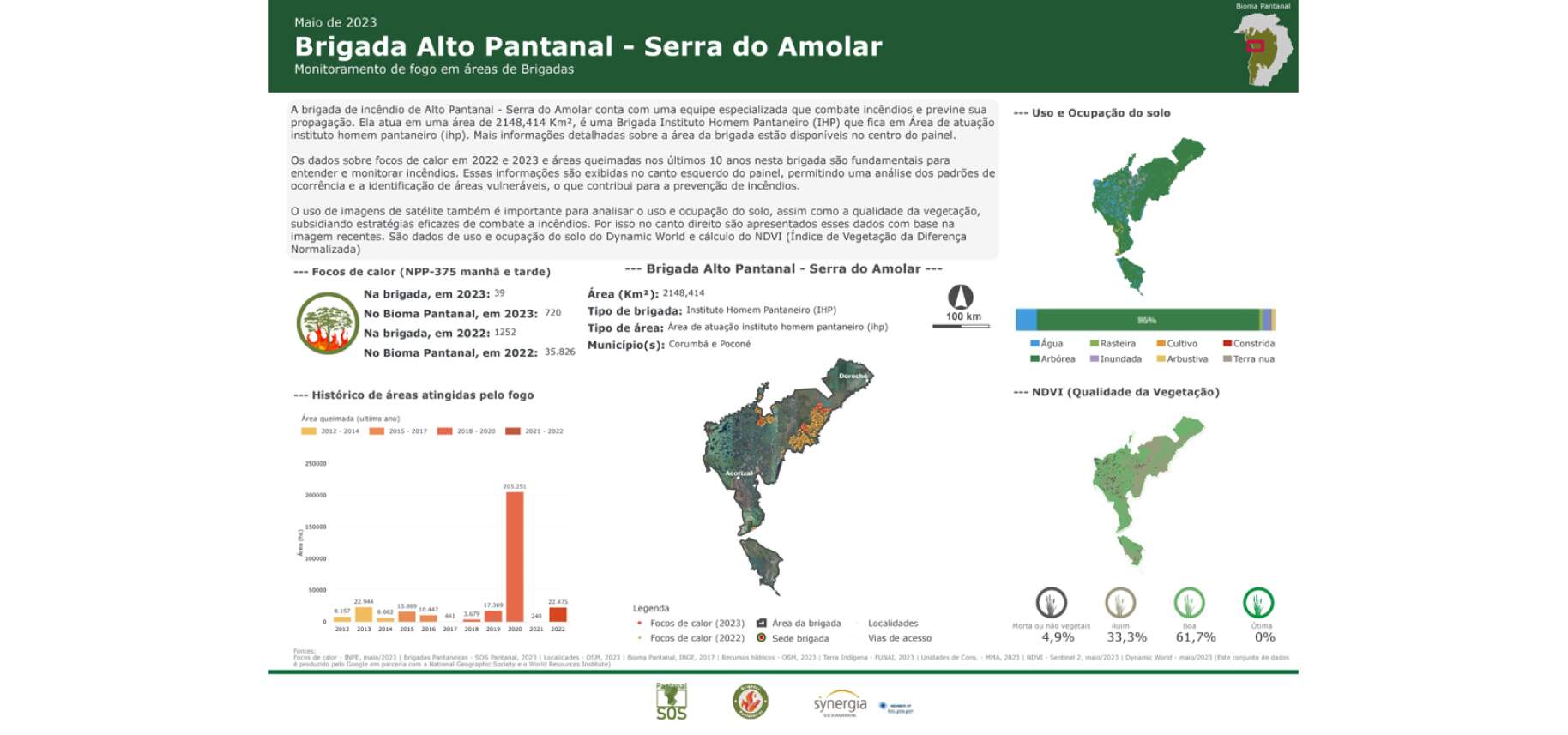
With bimonthly productions, each Panel per Brigade brings territorial information about a specific brigade, totaling 24 panels, containing data on land use and occupation, the number of areas burned within the brigade over the last 10 years, the location of fire outbreaks heat and other information within the brigade area and vegetation quality data (NDVI).

From the perspective of experts from the Synergia Study Center and the company’s Studies and Research Directorate , the Aracuã Panel stands out for bringing data from hot spot monitoring in an accessible way , in addition to working with information recorded practically in real time .
Marcos Vinicius Quizados de Lima, Geoprocessing specialist at Synergia, also highlights the importance of dealing with such up-to-date information : “The main difference of the panel is having the information in almost real time. It is not possible to apply an action in a gigantic territory, where almost everything has some risk, without planning. And the analysis seen in a more real, and more recent way, brings the possibility of more assertive decisions, saves resources and facilitates the management of the area where corrective actions will be positioned, saving time and reducing damage”, he points out.
According to Leonardo Gomes, executive director of the SOS Pantanal Institute, “Aracuã management panels are a fundamental part of the SOS Pantanal Integrated Fire Management strategy. Thanks to Synergia’s technical support, we were able to monitor the evolution of outbreaks, burned area, soil conditions, vegetation and mainly the results of each brigade’s actions. With this tool, the brigades themselves can have a visual idea of the results of their work, evaluating their efforts, engaging more people and planning improvements in the next actions”.


Sign up and receive our news.